Losing a critical Excel file can be a stressful experience especially when it’s nowhere to be found in the Recycle Bin. Perhaps you deleted it permanently using Shift + Delete, the file disappeared after a crash, or it was stored on a removable drive. Whatever the cause, there’s no need to panic. In most cases, a deleted Excel file can still be recovered, even if it isn’t visible in the Recycle Bin.
Why Excel Files Might Not Be in the Recycle Bin
Before diving into recovery methods, it’s important to understand why an Excel file may not show up in the Recycle Bin. Here are common reasons:
Shift + Delete: Files deleted using this keyboard shortcut bypass the Recycle Bin and are immediately marked for removal.
Deleted from External Devices: Files removed from USB drives, SD cards, or external hard drives do not go to the Recycle Bin.
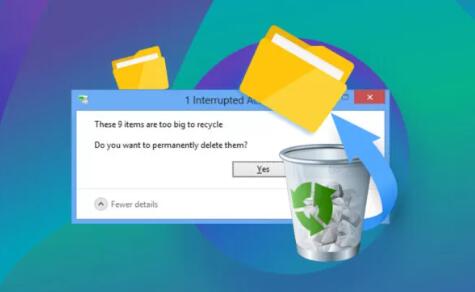
Large File Sizes: Files larger than the allocated Recycle Bin space are deleted permanently.
Emptied Recycle Bin: If you deleted the file and later emptied the Recycle Bin, it will no longer appear there.
Automatic Cleanup Tools: Disk cleanup utilities or third-party optimizers may have cleared the file.
File Stored in Temporary Folder: Some Excel files are stored temporarily and may disappear after a crash or reboot.
Understanding the cause helps you choose the best recovery path.
Immediate Actions After Deletion
Time is of the essence when retrieving deleted Excel files. The longer you use your computer after deletion, the more likely it is that Windows will overwrite the space once occupied by the lost file.
Take These Steps Immediately:
Stop saving new files on the same drive where the Excel file was deleted.
Avoid installing recovery software on that same drive.
Create a backup image of the drive if the file is critical and you want to try multiple recovery methods.
Now, let’s walk through the most effective strategies to get your file back.
Method 1: Search for AutoRecover Files in Excel
Excel has a built-in AutoRecover feature that can help you retrieve unsaved or recently deleted files.
To search for AutoRecover files:
Open Microsoft Excel.
Go to File > Info.
Look for a button that says Manage Workbook.
Click Recover Unsaved Workbooks.
Browse through the list of available files and open the one you need.
Save it to a new location.
If the file was never saved but was lost during a crash or reboot, this method often works.
Method 2: Search for Temporary Files
Sometimes, Excel creates temporary files while you work on a spreadsheet. These can serve as recovery points even if the original file is deleted.
To search for Excel temp files:
Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
Type %temp% and press Enter.
Look for files with names like ~Excel, .tmp, or with a .bak extension.
Sort by date and identify the one most likely associated with your lost file.
Open it in Excel to verify contents, then save a copy.
Temporary files might not have the same filename as your original file but can still contain your data.
Method 3: Restore a Previous Version
If File History or System Restore is enabled, you may be able to restore a previous version of the folder where the Excel file was stored.
To restore a previous version:
Navigate to the folder where the Excel file was stored.
Right-click the folder and select Restore previous versions.
Select a version that predates the file’s deletion.
Click Open to view the contents.
If the Excel file is there, copy it to a new location.
This feature depends on system protection being enabled or File History being turned on.
Method 4: Use Windows File History
If you’ve set up File History, Windows periodically backs up files and folders, allowing for targeted recovery.
To use File History:
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Backup.
Click More options > Restore files from a current backup.
Use the timeline to browse previous backups.
Find and restore your Excel file.
Even if your Recycle Bin is empty, File History may hold the version you need.
Method 5: Recover from OneDrive or Other Cloud Storage
If your Excel file was synced with OneDrive, Google Drive, or Dropbox, it may still exist in the cloud’s recycle bin or trash.
To restore from OneDrive:
Log in to OneDrive.com.
Go to the Recycle Bin in the left sidebar.
Search for your Excel file.
Select and click Restore.
Other cloud services have similar features with their own trash folders or version history tools.
Method 6: Use Data Recovery Software
Panda Data Recovery
When an Excel file is deleted, the data often remains on the drive, just marked as free space. Until that space is overwritten, the file can be recovered. Panda Data Recovery is designed to scan deep into your hard drive, USB, or SD card to locate and restore Excel files that no longer appear in the Recycle Bin.
Using Panda Data Recovery is easy. Install the software on a different drive to avoid overwriting the deleted file. Then, launch the program, select the drive where your Excel file was stored, and start a scan. You can choose between a quick scan for recent deletions or a deep scan for harder-to-find files.
Once the scan completes, you can preview recoverable Excel files even those with .xls or .xlsx extensions—before restoring them. Panda also supports recovery from formatted or corrupted drives, making it useful in cases of accidental formatting or device errors.
Method 7: Check Excel’s Recent Files List
If you worked on the file recently, Excel’s Recent Files list might help you track its original location.
To access the recent file list:
Open Excel.
Go to File > Open > Recent.
Review the list and try to open files from known locations.
If the file cannot be opened, right-click and copy the path for recovery attempts.
Sometimes the file path alone can help you trace temp versions or backups.
Method 8: Restore from a Backup
If you manually back up your files or use backup tools like Macrium Reflect, Acronis, or Windows Backup, restore the file from your backup.
Steps vary by tool, but most involve:
Launching the backup software.
Selecting a recovery point before the file was lost.
Browsing to the Excel file and restoring it.
This method is reliable, assuming regular backups are in place.
Method 9: Contact IT or Recovery Professionals (For Business or Critical Files)
If you’ve exhausted all methods and the file is extremely valuable—such as a financial report, legal document, or major project—professional recovery may be necessary.
Signs you should contact data recovery professionals:
The drive isn’t recognized by your computer.
You hear unusual sounds from the hard drive.
The file system is showing as RAW or unformatted.
Multiple recovery tools have failed to retrieve the file.
Professionals use cleanroom technology and advanced imaging tools to recover data even from damaged or corrupted drives.
Preventing Future Data Loss
After recovering your Excel file, take proactive steps to avoid future loss.
1. Enable AutoSave and AutoRecover in Excel:
Go to File > Options > Save.
Ensure AutoSave is on.
Set AutoRecover frequency to 1–5 minutes.
2. Set Up File History or Backup Software:
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Backup.
Use File History to back up files automatically.
Consider tools like Macrium Reflect or Acronis for full image backups.
3. Use Cloud Storage with Version History:
Services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox store multiple file versions.
If something is deleted or changed, you can roll back.
4. Avoid Saving to External Drives Without Backups:
Excel files on USB drives or memory cards are not protected by Windows recovery systems.
5. Be Careful with Disk Cleaners and Optimizers:
These tools may erase temp files and AutoRecover files if not configured properly.
About us and this blog
Panda Assistant is built on the latest data recovery algorithms, ensuring that no file is too damaged, too lost, or too corrupted to be recovered.
Request a free quote
We believe that data recovery shouldn’t be a daunting task. That’s why we’ve designed Panda Assistant to be as easy to use as it is powerful. With a few clicks, you can initiate a scan, preview recoverable files, and restore your data all within a matter of minutes.

 Try lt Free
Try lt Free Recovery success rate of up to
Recovery success rate of up to









